- Java层的Binder对学习Framework层的源码有很大的帮助;
一.进程间通信的基本原理
1.Binder是什么
- IPC的机制(面试这样回答是不够的,这里只考虑对进程间通信学习的理解)
2.什么时候要使用到进程间通信
- AMS和ActivityThread之间的通信等等;
- 项目中的使用场景(建议单独开进程);
- 1.WebView加载
- 2.图片加载(下载图片是非常耗内存的,另外一个进程的话本地的进程安全性更有保障)
- 下载的进程很容易出错,即便是下载的进程挂掉了,但是不会影响主进程;
- 3.推送
- 4.双进程守护
- 像一些系统服务,获取输入法服务、闹钟服务、摄像头服务、电话服务,都是需要进程间的通讯;
- 大型项目都会使用到多进程;
3.为什么要多进程
- 虚拟机分配给每一个应用的内存是有限制的(每一个进程的内存大小存在限制);
4.进程间通信为什么要用到Binder
- 主要是基于性能、稳定性和安全性几方面的原因(详细请看《AMS服务执行流程》一文)。
二.Android增加Binder的原因
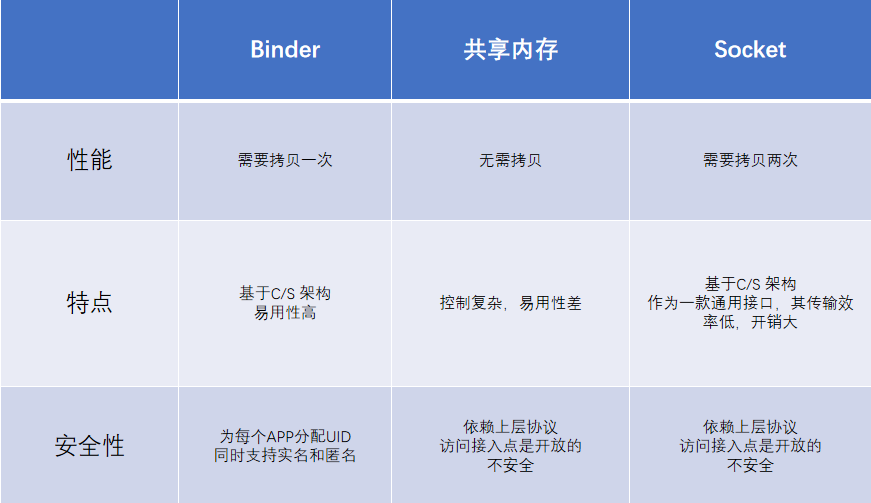
1.Binder与传统IPC对比
- 这里只列出了比较有代表性的几种
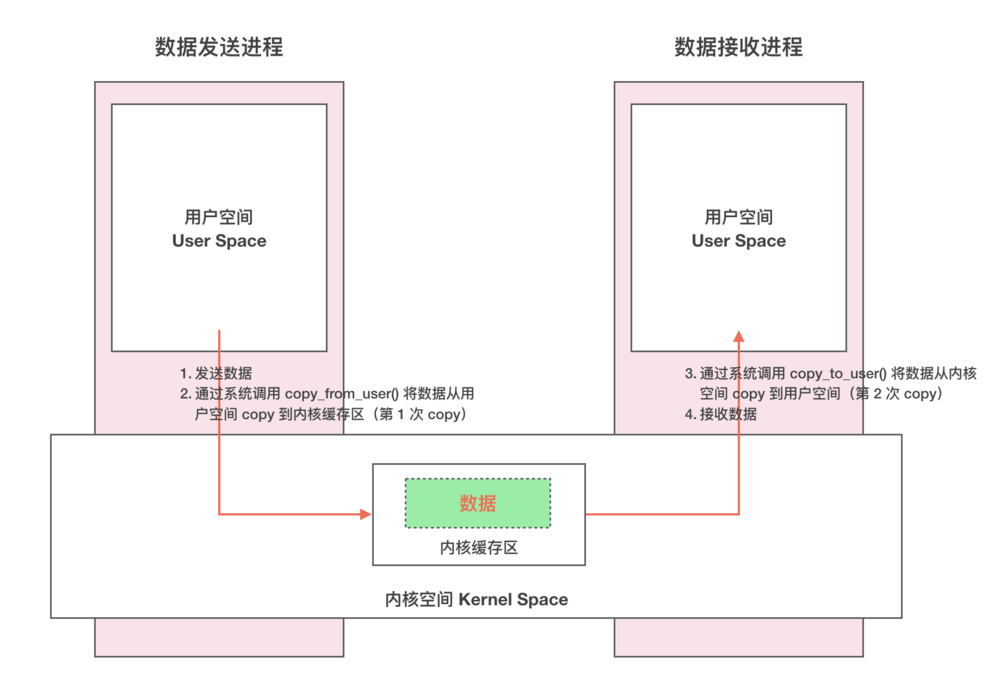
2.Binder拷贝一次的解释
- 传统的IPC传输数据
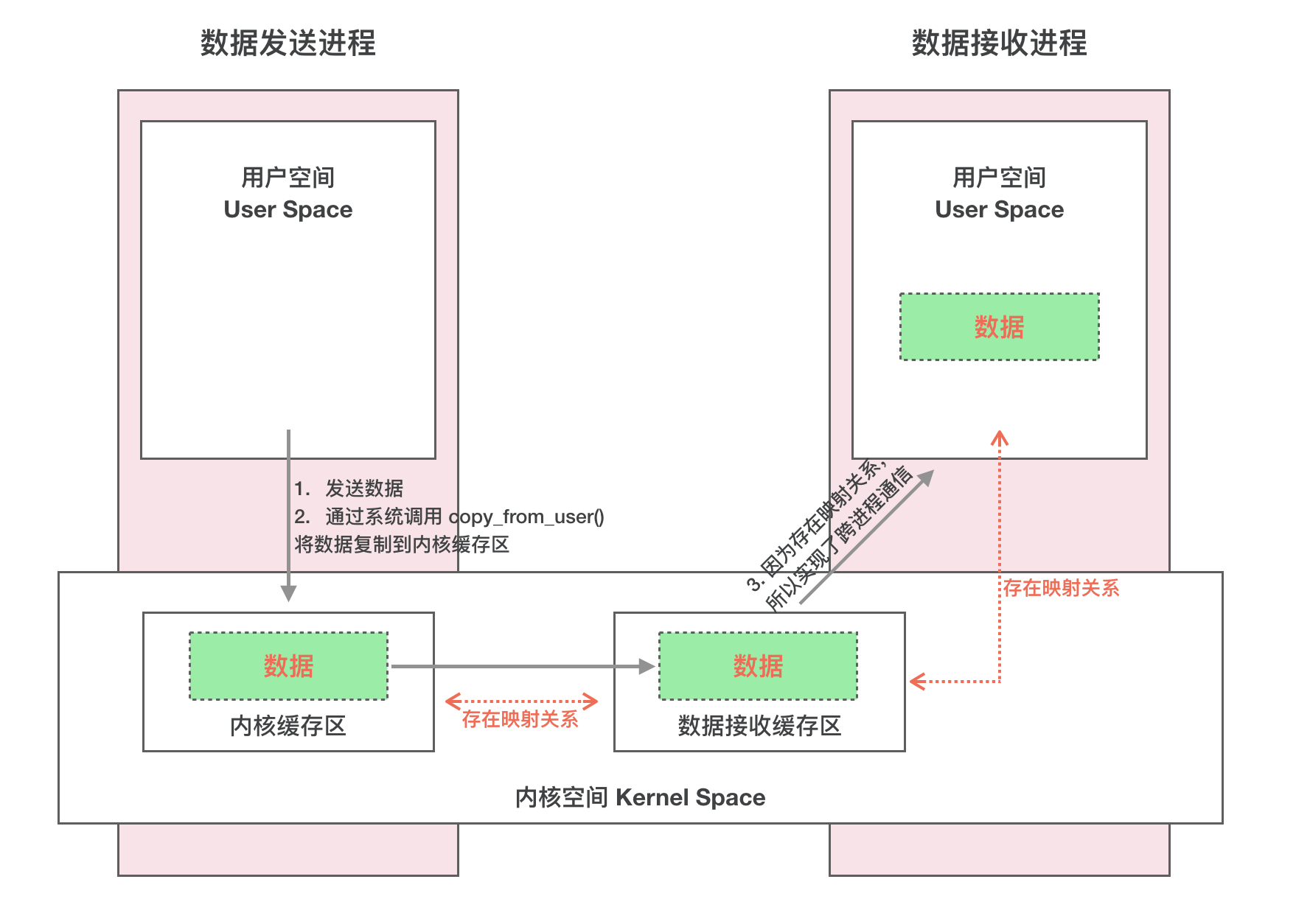
- 服务端的空间和内核空间都会映射到同一个地方(通过mmap机制,将内核空间和用户空间都映射到同一块物理内存。共享内存无需拷贝的解释:实现发送端、接收端和内核空间都在一块物理空间,也是通过mmap实现的)
3.选择Binder的原因
- 既然共享内存通过mmap实现三端都映射到同一块内存,那为什么Binder不这么做?
- 共享内存,将客户端和服务端映射到同一块内存,需要同步机制(比较容易出现数据不同步,死锁等问题),从而控制比较复杂,开销大。而采用C/S架构,易用性高,故Binder才选择了一次拷贝,相对而言牺牲了一点性能;
- mmap,简单理解:虚拟地址映射到物理地址;
- 为什么不选择Socket:Socket作为通用的接口,其传输效率是比较低的,主要是跨网络的通信。而进程的通信是高速的;
- 最主要的一点,安全性;
- PID是进程间唯一的标识,共享内存,Socket是通过上层协议。如Socket传输数据,一般是把数据打包成一个包,PID是放在包里面的,那么系统看到的PID由App控制。
- 而Binder的PID和UID是系统分配的;
- Binder还支持实名和匿名;
三.源码分析
-
AIDL的源码分析,从如何获得另外一个进程的对象 的角度来分析
- 1.客户端如何获取到AIDL的句柄的
- 2.通过这个句柄是如何调到服务端的呢
- 3.服务端又是如何做处理的
-
查看AIDL文件的结构
- Stub类:抽象类,继承自Binder,实现了定义的AIDL接口
- Proxy类:实体类,实现了定义的AIDL接口
1.获取AIDL接口的方法
//点击查看
ILeoAidl.Stub.asInterface(service)
//在不同进程,得到Proxy对象(用来发送数据)
//客户端拿到句柄之后
// _data和_reply包
//调用方法传的参数
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
//服务端返回的数据
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
//校验:每一个服务不止一个AIDL
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
//将传输的数据写入到包里面
_data.writeInt(1);
person.writeToParcel(_data, 0);
//关键性的代码
//调用之后,客户端会把线程挂起来,直到服务端有数据返回,客户端线程才会继续运行
//参数4;0,表示客户端可以发送到服务端,,服务端可以返回
//1.客户端发到服务端,服务端不以返回
//调用transact方法后,就到了Binder---> 然后就会调用服务端的Stub类的onTransact方法
//transact的底层原理是在c里面,暂时不做深入研究
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_addPerson, _data, _reply, 0);
//服务端有数据处理异常,也会写入
_reply.readException();
- 在服务端,描述符被初始化。在客户端描述符并不会初始化。比较描述符的原因:客户端和服务端有可能是在同一个进程,在同一个进程则不需要经过Binder;
- 分析服务端的Stub类的onTransact方法
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR;
switch (code) {
//...
case TRANSACTION_addPerson: {
data.enforceInterface(descriptor);
com.xx.leo_service.Person _arg0;
if ((0 != data.readInt())) {
_arg0 = com.xx.leo_service.Person.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
} else {
_arg0 = null;
}
//调用具体实现类的addPerson方法,即定义的服务类中的Binder类(new ILeoAidl.Stub())的addPerson方法
//到此就实现了,从客户端到服务端的调用
//服务端通过reply进行返回
this.addPerson(_arg0);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
//...
}
}
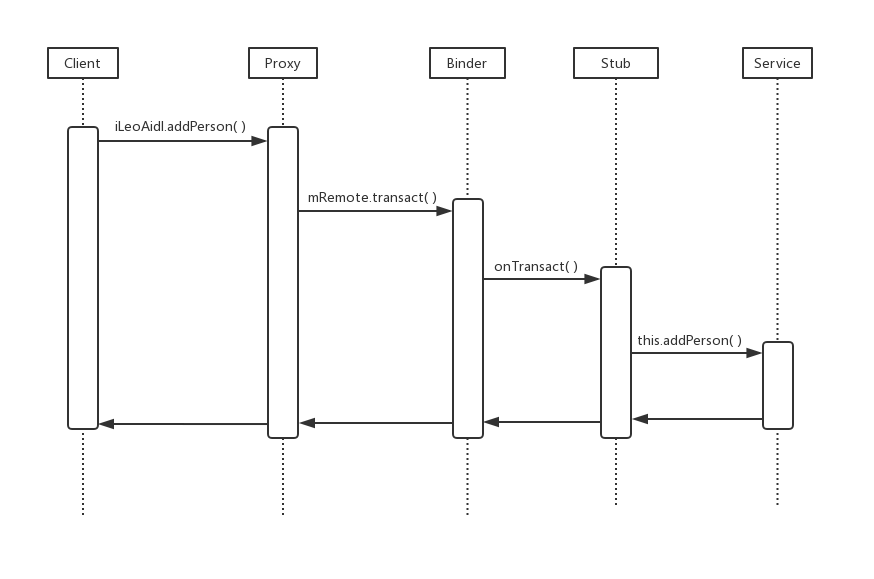
- 总结,客户端到服务端的时序图
2.如何通过bindService去绑定服务的
- 源码分析(sdk版本 = 28)
2.1.bindService分析
//ContextWrapper类
Context mBase;
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
//调用Context实现类
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
- ContextImpl实现类
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, mMainThread.getHandler(), getUser());
}
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
//...
//调用AMS的bindService
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
//...
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
- 分析AMS的bindService
//内部执行的事情
//创建服务,绑定服务
public int bindService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage,
int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
//进行了一个同步的处理
synchronized(this) {
//分析bindServiceLocked
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
- ActiveServices的bindServiceLocked
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
try {
//...
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//分析1
//a进程访问b进程
//b进程没有启动 是如何执行的
//b进程启动了,但是service没有创建出来
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
//...
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
//...
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
//分析2 绑定服务 分两种情况
//之前没有绑定服务,回调onBind
//之前绑定服务,调用onRebind
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
}
//...
}
//...
return 1;
}
- 分析bringUpServiceLocked
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
//app已经创建了
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
//分析
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
}
//...
}
}
//app没有启动
//分析startProcessLocked,
//===》startProcessLocked(会有多个重载方法调用)
//===》startProcess
//最终通过Process.start创建了进程
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
hostingType, r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
String msg = "Unable to launch app "
+ r.appInfo.packageName + "/"
+ r.appInfo.uid + " for service "
+ r.intent.getIntent() + ": process is bad";
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
//...
}
- 分析realStartServiceLocked
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
//...
try {
//...
//分析
//调用ActivityThread的ApplicationThread的方法
//最终调用handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
}
//...
}
- handleCreateService
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
//通过类加载 + 反射创建service
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//调用service的 attach onCreate
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService());
service.onCreate();
//单例
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
- 返回分析requestServiceBindingLocked方法
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
//...
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//绑定服务
//最终调用
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
if (!rebind) {
i.requested = true;
}
i.hasBound = true;
i.doRebind = false;
}
//...
}
return true;
}
- ActivityThread类的handleBindService方法
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
//接口回调 自定义服务中的onBind方法
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
//分析AMS的publishService
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
- AMS的publishService
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
//分析publishServiceLocked
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
- 分析publishServiceLocked
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList<ConnectionRecord> clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i<clist.size(); i++) {
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Not publishing to: " + c);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Bound intent: " + c.binding.intent.intent);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Published intent: " + intent);
continue;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Publishing to: " + c);
try {
//最终调用 客户端的onServiceConnected
c.conn.connected(r.name, service, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + r.name +
" to connection " + c.conn.asBinder() +
" (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
3.分析ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected调用
- 需要倒推
- c.conn = IServiceConnection conn,找到IServiceConnection的实现类即可
//回到bindService开始分析--->ContextImpl类的bindServiceCommon
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler
handler, UserHandle user) {
//...
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
}
//...
}
//分析LoadedApk类的getServiceDispatcher方法
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {
synchronized (mServices) {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = null;
ArrayMap<ServiceConnection, LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> map = mServices.get(context);
if (map != null) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Returning existing dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);
sd = map.get(c);
}
if (sd == null) {
//分析ServiceDispatcher类,传入了ServiceConnection参数
sd = new ServiceDispatcher(c, context, handler, flags);
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Creating new dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<>();
mServices.put(context, map);
}
map.put(c, sd);
} else {
sd.validate(context, handler);
}
//通过getIServiceConnection可以得知IServiceConnection的实现类是ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
}
//ServiceDispatcher类
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
private final ServiceConnection mConnection;
//...
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
//即IServiceConnection的实现类是InnerConnection
//最终触发的是connected
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
//分析
sd.connected(name, service, dead);
}
}
}
//...
ServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection conn,
Context context, Handler activityThread, int flags) {
mIServiceConnection = new InnerConnection(this);
mConnection = conn;
mContext = context;
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mLocation = new ServiceConnectionLeaked(null);
mLocation.fillInStackTrace();
mFlags = flags;
}
//...
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else {
doConnected(name, service, dead);
}
}
//...
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
// We unbound before receiving the connection; ignore
// any connection received.
return;
}
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
// Huh, already have this one. Oh well!
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don't do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
// The named service is being disconnected... clean up.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is now disconnected.
if (old != null) {
//最终的调用
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
if (dead) {
mConnection.onBindingDied(name);
}
// If there is a new viable service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
//最终的调用
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
} else {
// The binding machinery worked, but the remote returned null from onBind().
mConnection.onNullBinding(name);
}
}
//...
}


评论区